- Color Education
-
Color Knowledge
-
Current position:
Home>
Color Knowledge
what is spectrophotometry?
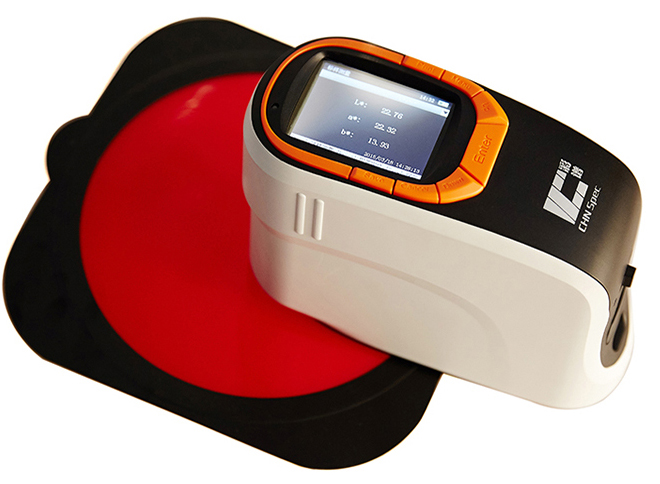

Spectrophotometric method is a method for qualitative and quantitative analysis of the substance by measuring the absorbance of the light at a certain wavelength or wavelength range. It has the advantages of high sensitivity, simple operation and fast, and is the most commonly used experimental method in biochemical experiments. Many substances are determined by spectrophotometry. In the spectrophotometer, the absorption intensity corresponding to different wavelength can be obtained when the light of different wavelengths is continuously irradiated to a certain concentration of sample solution.
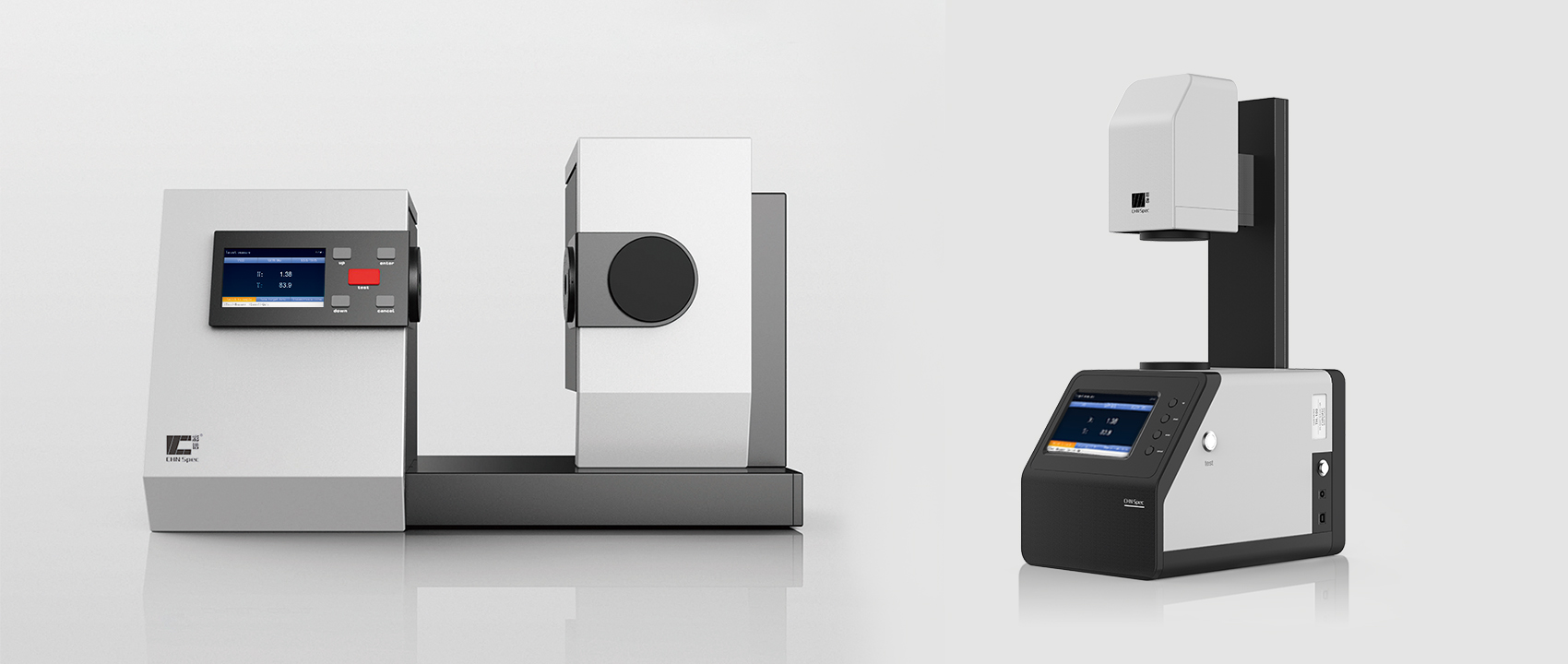
The use of spectrophotometers spans various scientific fields, such as physics, materials science, chemistry, biochemistry, and molecular biology. They are widely used in many industries including semiconductors, laser and optical manufacturing, printing and forensic examination, as well in laboratories for the study of chemical substances. Spectrophotometry is often used in measurements of enzyme activities, determinations of protein concentrations, determinations of enzymatic kinetic constants, and measurements of ligand binding reactions. Ultimately, a spectrophotometer is able to determine, depending on the control or calibration, what substances are present in a target and exactly how much through calculations of observed wavelengths.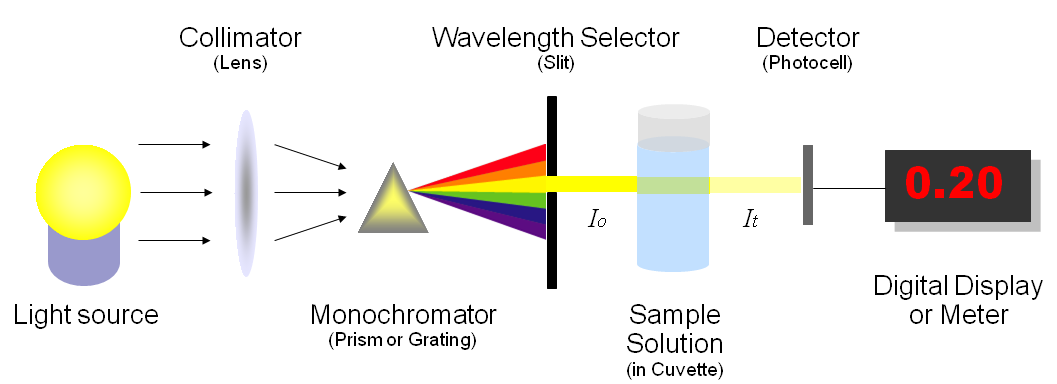
A spectrophotometer is commonly used for the measurement of transmittance or reflectance of solutions, transparent or opaque solids, such as polished glass, or gases. Although many biochemicals are colored, as in, they absorb visible light and therefore can be measured by colorimetric procedures, even colorless biochemicals can often be converted to colored compounds suitable for chromogenic color-forming reactions to yield compounds suitable for colorimetric analysis. However, they can also be designed to measure the diffusivity on any of the listed light ranges that usually cover around 200 nm - 2500 nm using different controls and calibrations. Within these ranges of light, calibrations are needed on the machine using standards that vary in type depending on the wavelength of the photometric determination.For the products produced by our company using spectrophotometry, there are many fields that can be applied, including food, printing, textile and other industries, which have been widely used.










